Stanford researchers have developed a novel phantom which can integrate quality assurance (QA) procedures for radiofrequency tracking system, surface mapping system, Winston-Lutz test, the imaging system isocenter test and laser verification.
By combining these QA tests into a single phantom, this product provides an independent QA method from the vendor, reduces the number of phantoms required for QA, reduces the time required of a medical physicist to perform these QA tasks, and increases the reproducibility of phantom placement. Moreover, this phantom is the first and only phantom which can QA the rotational accuracy of the radiofrequency tracking system and surface mapping system. Most importantly, it is feasible to evaluate the deviation of isocenter between the individual systems.
Figure 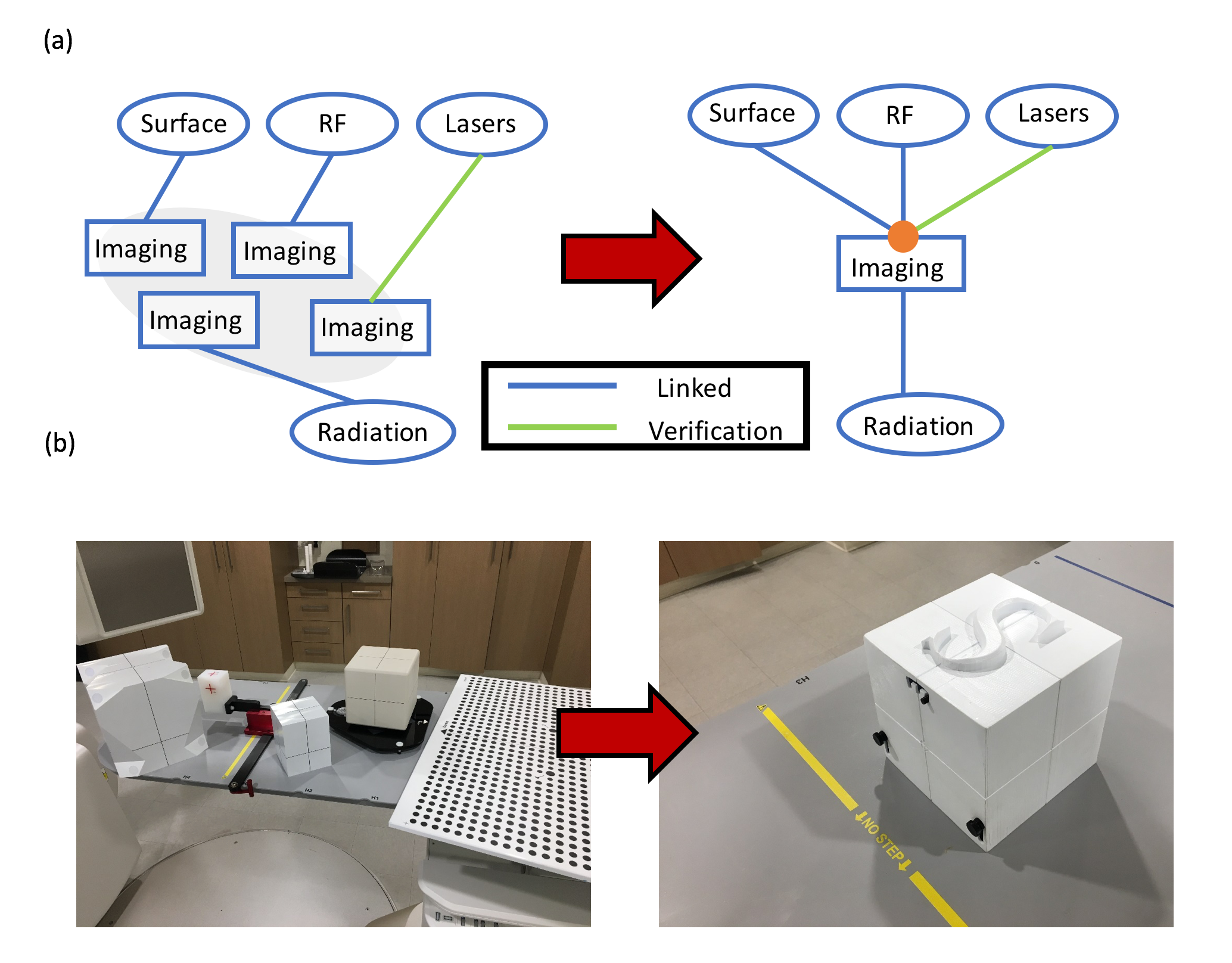
Figure description - The improvement of the integrated phantom. (a) Uncertainty introduced by the reproducibility of quality assurance (QA) phantom setup (left) and the reduction of uncertainty with the single isocentric QA phantom and procedure (right). With the use of this integrated phantom, it is possible to reveal the deviation of the isocenters from each system. (b) The space to store the QA phantoms can grow very quickly with the number of phantoms required for the QA procedures (left) compared to one single phantom can do it all (right). Note: RF: radiofrequency tracking system, Surface: surface mapping system, and Radiation: Winston-Lutz test.
Stage of Research Prototype completed
Studies showed promising results as compared to vendor’s phantoms
Scope of pending patent has exclusive quality assurance coverage of the listed radiotherapy technologies